 1.React基本使用
1.React基本使用
# 1.React使用-考点
# 1.1 React vs Vue
React和Vue一样重要(特别是大厂面试),力求两者都会
React和Vue有很多相通之处,而且正在趋于一致
React比Vue学习成本高,尤其对于初学者
# 1.2 React使用
- 基本使用–常用,必须会
- 高级特性–不常用,但体现深度
- Redux和React-router使用
# 1.3 前置思考题
React组件如何通讯
JSX本质是什么
context是什么?有何用途
shouldComponentUpdate的用途
描述redux单项数据流
setState是同步还是异步?(场景题)
class Root extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props) this.state = { count: 0 } } } componentDidMount() { this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }) console.log(this.state.count)//打印 this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }) console.log(this.state.count)//打印 setTimeout(function(){ this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }) console.log(this.state.count)//打印 }, 0) setTimeout(function(){ this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }) console.log(this.state.count)//打印 }, 0) } render() { return <h1>{this.state.count}</h1> } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 2.React基本使用
- 日常使用,必须掌握,面试必考(不一定全考)
- 梳理知识点,从冗长的文档中摘出考点和重点
- 考察形式不限(参考后面的面试真题),但都在范围之内
# 2.1 JSX基本知识
变量、表达式
class style子元素和组件
import React from 'react'
import './style.css'
import List from '../List'
class JSXBaseDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
name: 'uploadhub',
imgUrl: 'https://xxx.com/xxx.jpg',
flag: true
}
}
render() {
// 获取变量 插值
const pElem = <p>{this.state.name}</p>
return pElem
// 表达式
const exprElem = <p>{this.state.flag ? 'yes' : 'no'}</p>
return exprElem
// 子元素
const imgElem = <div>
<p>我的头像</p>
<img src="xxx.png"/>
<img src={this.state.imgUrl}/>
</div>
return imgElem
// class
const classElem = <p className="title">设置 css class</p>
return classElem
// style
const styleData = { fontSize: '30px', color: 'blue' }
const styleElem = <p style={styleData}>设置 style</p>
// 内联写法,注意 {{ 和 }}
// const styleElem = <p style={{ fontSize: '30px', color: 'blue' }}>设置 style</p>
return styleElem
// 原生 html
const rawHtml = '<span>富文本内容<i>斜体</i><b>加粗</b></span>'
const rawHtmlData = {
__html: rawHtml // 注意,必须是这种格式
}
const rawHtmlElem = <div>
<p dangerouslySetInnerHTML={rawHtmlData}></p>
<p>{rawHtml}</p>
</div>
return rawHtmlElem
// 加载组件
const componentElem = <div>
<p>JSX 中加载一个组件</p>
<hr/>
<List/>
</div>
return componentElem
}
}
export default JSXBaseDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
# 2.2 条件判断
ifelse- 三元表达式
- 逻辑运算符
&&||
import React from 'react'
import './style.css'
class ConditionDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
theme: 'black'
}
}
render() {
const blackBtn = <button className="btn-black">black btn</button>
const whiteBtn = <button className="btn-white">white btn</button>
// // if else
// if (this.state.theme === 'black') {
// return blackBtn
// } else {
// return whiteBtn
// }
// // 三元运算符
// return <div>
// { this.state.theme === 'black' ? blackBtn : whiteBtn }
// </div>
// &&
return <div>
{ this.state.theme === 'black' && blackBtn }
</div>
}
}
export default ConditionDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 2.3 渲染列表
map:map返回一个重组数组key:性能优化要求有key属性,与diff算法有关
import React from 'react'
class ListDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
list: [
{
id: 'id-1',
title: '标题1'
},
{
id: 'id-2',
title: '标题2'
},
{
id: 'id-3',
title: '标题3'
}
]
}
}
render() {
return <ul>
{ /* vue v-for */
this.state.list.map(
(item, index) => {
// 这里的 key 和 Vue 的 key 类似,必填,不能是 index 或 random
return <li key={item.id}>
index {index}; id {item.id}; title {item.title}
</li>
}
)
}
</ul>
}
}
export default ListDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# 2.4 事件
bind this
关于event参数
传递自定义参数
# 2.4.1 React事件为何要bind this
import React from 'react'
class EventDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
name: 'zhangsan',
list: [
{
id: 'id-1',
title: '标题1'
},
{
id: 'id-2',
title: '标题2'
},
{
id: 'id-3',
title: '标题3'
}
]
}
// 修改方法的 this 指向,在这边bind初始化时一次就好,性能好,在点击DOM上bind每次点击都要bind一次
this.clickHandler1 = this.clickHandler1.bind(this)
}
render() {
// // this - 使用 bind
// return <p onClick={this.clickHandler1}>
// {this.state.name}
// </p>
// // this - 使用静态方法
// return <p onClick={this.clickHandler2}>
// clickHandler2 {this.state.name}
// </p>
// // event
// return <a href="https://xxx.com/" onClick={this.clickHandler3}>
// click me
// </a>
// 传递参数 - 用 bind(this, a, b)
return <ul>{this.state.list.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={item.id} onClick={this.clickHandler4.bind(this, item.id, item.title)}>
index {index}; title {item.title}
</li>
})}</ul>
}
clickHandler1() {
// console.log('this....', this) // this 默认是 undefined
this.setState({
name: 'lisi'
})
}
// 静态方法,this 指向当前实例
clickHandler2 = () => {
this.setState({
name: 'lisi'
})
}
// 获取 event
clickHandler3 = (event) => {
event.preventDefault() // 阻止默认行为
event.stopPropagation() // 阻止冒泡
console.log('target', event.target) // 指向当前元素,即当前元素触发
console.log('current target', event.currentTarget) // 指向当前元素,假象!!!
// 注意,event 其实是 React 封装的。可以看 __proto__.constructor 是 SyntheticEvent ,即组合事件
console.log('event', event) // 不是原生的 Event
console.log('event.__proto__.constructor', event.__proto__.constructor)
// 原生 event 如下。其 __proto__.constructor 是 MouseEvent
console.log('nativeEvent', event.nativeEvent)
console.log('nativeEvent target', event.nativeEvent.target) // 指向当前元素,即当前元素触发
console.log('nativeEvent current target', event.nativeEvent.currentTarget) // 指向 document !!!
}
// 传递参数
clickHandler4(id, title, event) {
console.log(id, title)
console.log('event', event) // 最后追加一个参数,即可接收 event
}
}
export default EventDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
# 2.4.2 React事件和DOM事件的区别
- event 是
SyntheticEvent,模拟出来 DOM 事件所有能力 event.nativeEvent是原生事件对象- 所有的React事件,都被挂载到 document 上
- 和 DOM 事件不一样,和 Vue 事件也不一样
# 2.4.3 React17后事件绑定到root上
- React 16及以前是绑定到 document上
- React 17后React事件绑定到 root 组件
- 有利于多个React版本并存,例如微前端
# 2.5 表单
受控组件:
input的值受state影响input textarea select用``value`checkbox radio用checked
import React from 'react'
class FormDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
name: 'uploadhub',
info: '个人信息',
city: '深圳',
flag: true,
gender: 'male'
}
}
render() {
// // 受控组件(非受控组件,后面再讲)
// return <div>
// <p>{this.state.name}</p>
// <label htmlFor="inputName">姓名:</label> {/* 用 htmlFor 代替 for */}
// <input id="inputName" value={this.state.name} onChange={this.onInputChange}/>
// </div>
// textarea - 使用 value
return <div>
//被备注掉的这行写法是错的
//<textarea>{this.state.info}</textarea>
//这行才对
<textarea value={this.state.info} onChange={this.onTextareaChange}/>
<p>{this.state.info}</p>
</div>
// // select - 使用 value
// return <div>
// <select value={this.state.city} onChange={this.onSelectChange}>
// <option value="beijing">北京</option>
// <option value="shanghai">上海</option>
// <option value="shenzhen">深圳</option>
// </select>
// <p>{this.state.city}</p>
// </div>
// // checkbox
// return <div>
// <input type="checkbox" checked={this.state.flag} onChange={this.onCheckboxChange}/>
// <p>{this.state.flag.toString()}</p>
// </div>
// // radio
// return <div>
// male <input type="radio" name="gender" value="male" checked={this.state.gender === 'male'} onChange={this.onRadioChange}/>
// female <input type="radio" name="gender" value="female" checked={this.state.gender === 'female'} onChange={this.onRadioChange}/>
// <p>{this.state.gender}</p>
// </div>
// 非受控组件 - 后面再讲
}
onInputChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
name: e.target.value
})
}
onTextareaChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
info: e.target.value
})
}
onSelectChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
city: e.target.value
})
}
onCheckboxChange = () => {
this.setState({
flag: !this.state.flag
})
}
onRadioChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
gender: e.target.value
})
}
}
export default FormDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
# 2.6 组件使用
props传递数据
props传递函数(这里和Vue的做法不同)
props类型检查
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class Input extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
title: ''
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<input value={this.state.title} onChange={this.onTitleChange}/>
<button onClick={this.onSubmit}>提交</button>
</div>
}
onTitleChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
title: e.target.value
})
}
onSubmit = () => {
const { submitTitle } = this.props
submitTitle(this.state.title) // 'abc'
this.setState({
title: ''
})
}
}
// props 类型检查
Input.propTypes = {
submitTitle: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
class List extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
const { list } = this.props
return <ul>{list.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={item.id}>
<span>{item.title}</span>
</li>
})}</ul>
}
}
// props 类型检查
List.propTypes = {
list: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.object).isRequired
}
class Footer extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
return <p>
{this.props.text}
{this.props.length}
</p>
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('footer did update')
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (nextProps.text !== this.props.text
|| nextProps.length !== this.props.length) {
return true // 可以渲染
}
return false // 不重复渲染
}
// React 默认:父组件有更新,子组件则无条件也更新!!!
// 性能优化对于 React 更加重要!
// SCU 一定要每次都用吗?—— 需要的时候才优化
}
class TodoListDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 状态(数据)提升
this.state = {
list: [
{
id: 'id-1',
title: '标题1'
},
{
id: 'id-2',
title: '标题2'
},
{
id: 'id-3',
title: '标题3'
}
],
footerInfo: '底部文字'
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<Input submitTitle={this.onSubmitTitle}/>
<List list={this.state.list}/>
<Footer text={this.state.footerInfo} length={this.state.list.length}/>
</div>
}
onSubmitTitle = (title) => {
this.setState({
list: this.state.list.concat({
id: `id-${Date.now()}`,
title
})
})
}
}
export default TodoListDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
# 2.7 setState
不可变值(
setState不能提前对state值进行修改,应该什么时候改就什么时候设值,而且设置的时候不能影响之前state的值)可能是异步更新
可能会被合并
import React from 'react'
class ListDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
render() {
return <p>{this.state.count}</p>
}
componentDidMount() {
// count 初始值为 0
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 })
console.log('1', this.state.count) // 0
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 })
console.log('2', this.state.count) // 0
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 })
console.log('3', this.state.count) // 2
})
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 })
console.log('4', this.state.count) // 3
})
}
}
export default ListDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
import React from 'react'
// 函数组件(后面会讲),默认没有 state
class StateDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 第一,state 要在构造函数中定义
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<p>{this.state.count}</p>
<button onClick={this.increase}>累加</button>
</div>
}
increase = () => {
// // 第二,不要直接修改 state ,使用不可变值 ----------------------------
// // this.state.count++ // 错误
// this.setState({
// count: this.state.count + 1 // SCU
// })
// 操作数组、对象的的常用形式
// 第三,setState 可能是异步更新(有可能是同步更新) ----------------------------
// this.setState({
// count: this.state.count + 1
// }, () => {
// // 联想 Vue $nextTick - DOM
// console.log('count by callback', this.state.count) // 回调函数中可以拿到最新的 state
// })
// console.log('count', this.state.count) // 异步的,拿不到最新值
// // setTimeout 中 setState 是同步的
// setTimeout(() => {
// this.setState({
// count: this.state.count + 1
// })
// console.log('count in setTimeout', this.state.count)
// }, 0)
// 自己定义的 DOM 事件,setState 是同步的。再 componentDidMount 中
// 第四,state 异步更新的话,更新前会被合并 ----------------------------
// // 传入对象,会被合并(类似 Object.assign )。执行结果只一次 +1
// this.setState({
// count: this.state.count + 1
// })
// this.setState({
// count: this.state.count + 1
// })
// this.setState({
// count: this.state.count + 1
// })
// 传入函数,不会被合并。执行结果是 +3
this.setState((prevState, props) => {
return {
count: prevState.count + 1
}
})
this.setState((prevState, props) => {
return {
count: prevState.count + 1
}
})
this.setState((prevState, props) => {
return {
count: prevState.count + 1
}
})
}
// bodyClickHandler = () => {
// this.setState({
// count: this.state.count + 1
// })
// console.log('count in body event', this.state.count)
// }
// componentDidMount() {
// // 自己定义的 DOM 事件,setState 是同步的
// document.body.addEventListener('click', this.bodyClickHandler)
// }
// componentWillUnmount() {
// // 及时销毁自定义 DOM 事件
// document.body.removeEventListener('click', this.bodyClickHandler)
// // clearTimeout
// }
}
export default StateDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
// -------------------------- 我是分割线 -----------------------------
// 不可变值(函数式编程,纯函数) - 数组
const list5Copy = this.state.list5.slice()
list5Copy.splice(2, 0, 'a') // 中间插入/删除
this.setState({
list1: this.state.list1.concat(100), // 追加
list2: [...this.state.list2, 100], // 追加
list3: this.state.list3.slice(0, 3), // 截取
list4: this.state.list4.filter(item => item > 100), // 筛选
list5: list5Copy // 其他操作
})
// 注意,不能直接对 this.state.list 进行 push pop splice 等,这样违反不可变值
// 不可变值 - 对象
this.setState({
obj1: Object.assign({}, this.state.obj1, {a: 100}),
obj2: {...this.state.obj2, a: 100}
})
// 注意,不能直接对 this.state.obj 进行属性设置,这样违反不可变值
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 2.7.1 setState⼀定是异步吗?(React18之前)
分成两种情况:
- 在组件⽣命周期或React合成事件中,setState是异步
- 在setTimeout或者原⽣dom事件中,setState是同步
//验证⼀:在setTimeout中的更新
changeText(){
setTimeout(()·=> {
this.setState({
message:"你好啊,李银河"
});
console.log(this.state.message);//你好啊,李银河
},0);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
验证⼆:原⽣DOM事件
componentDidMount(){
const btnEl =document.getElementById("btn");
btnEl.addEventListener('click' ,()=>{
this.setState({
message: "你好啊,李银河"
});
console.log(this.state.message);
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 2.7.2 setState默认是异步的(React18之后)
- 在React18之后,默认所有的操作都被放到了批处理中(异步处理)
- 如果希望代码可以同步会拿到,则需要执⾏特殊的flushSync操作
flushSync (()=>{
this.setState([ counter: 8888 })
})
console.log(this.state.counter)
2
3
4
# 2.8 组件生命周期
# 单组件生命周期
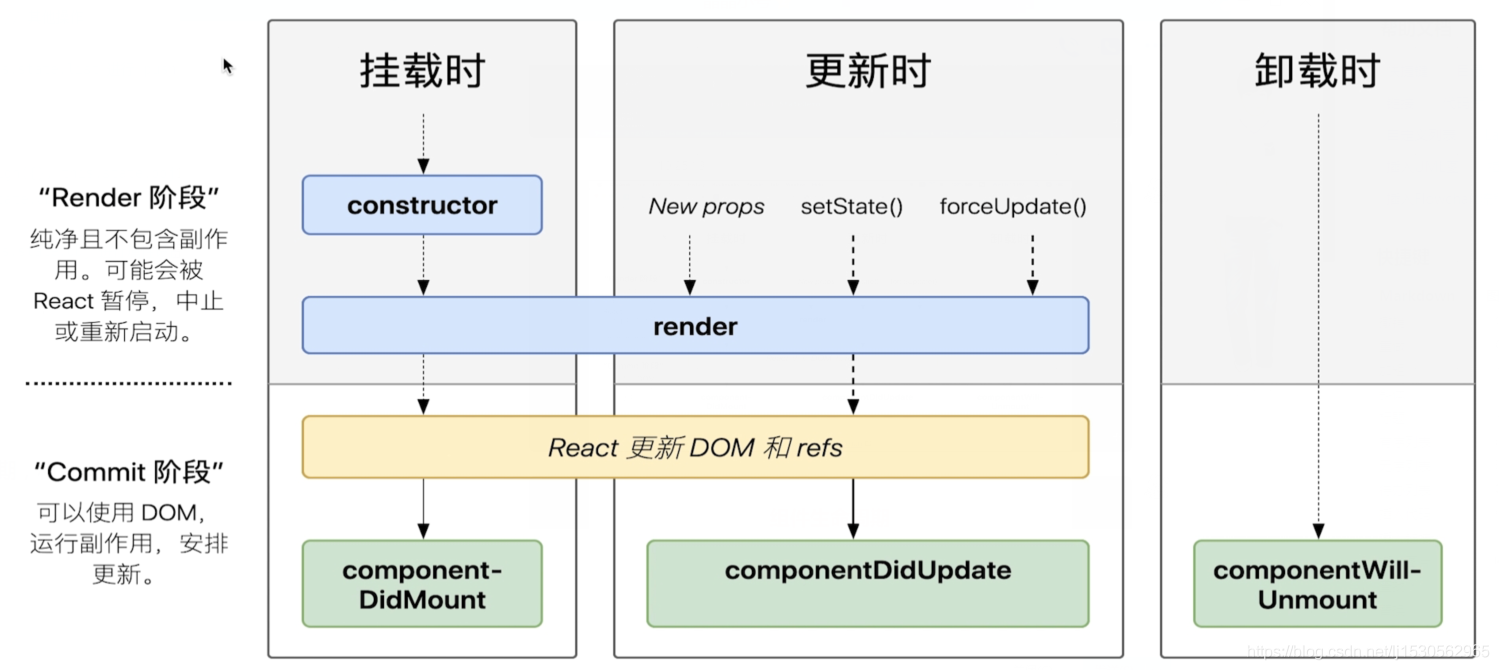
React 组件生命周期图示 (opens new window)
# 父子组件生命周期,和Vue的一样
# 3.React高级特性
- 不是每个都很常用,但用到的时候必须要知道
- 考察候选人对React的掌握是否全面,且有深度
- 考察做过的项目是否有深度和复杂度(至少能用到高级特性)
# 3.1 函数组件
纯函数,输入props,输出JSX
没有实例,没有生命周期,没有state
不能扩展其他方法
/*示例*/
//class 组件
class List extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
const { list } = this.props
return <ul>{
list.map((item, index) =>{
return <li key={item.id}>
<span>{item.title}</span>
</li>
})
}</ul>
}
}
//函数组件
function List(props){
const { list } = this.props
return <ul>{
list.map((item, index) =>{
return <li key={item.id}>
<span>{item.title}</span>
</li>
})
}</ul>
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 3.2 非受控组件
refdefaultValuedefaultChecked- 手动操作DOM元素
import React from 'react'
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
name: 'uploadhub',
flag: true,
}
this.nameInputRef = React.createRef() // 创建 ref
this.fileInputRef = React.createRef()
}
render() {
// // input defaultValue
// return <div>
// {/* 使用 defaultValue 而不是 value ,使用 ref */}
// <input defaultValue={this.state.name} ref={this.nameInputRef}/>
// {/* state 并不会随着改变 */}
// <span>state.name: {this.state.name}</span>
// <br/>
// <button onClick={this.alertName}>alert name</button>
// </div>
// // checkbox defaultChecked
// return <div>
// <input
// type="checkbox"
// defaultChecked={this.state.flag}
// />
// </div>
// file
return <div>
<input type="file" ref={this.fileInputRef}/>
<button onClick={this.alertFile}>alert file</button>
</div>
}
alertName = () => {
const elem = this.nameInputRef.current // 通过 ref 获取 DOM 节点
alert(elem.value) // 不是 this.state.name
}
alertFile = () => {
const elem = this.fileInputRef.current // 通过 ref 获取 DOM 节点
alert(elem.files[0].name)
}
}
export default App
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# 非受控组件-使用场景
必须手动操作DOM元素,setState实现不了
文件上传
<input type=file>某些富文本编辑器,需要传入DOM元素
# 受控组件 vs 非受控组件
优先使用受控组件,符合React设计原则
必须操作DOM时,再使用非受控组件
# 3.3 Portals
- 组件默认会按照既定层次嵌套渲染
- 如何让组件渲染到父组件以外?(使用Portals)
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import './style.css'
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
}
}
render() {
// // 正常渲染
// return <div className="modal">
// {this.props.children} {/* vue slot */}
// </div>
// 使用 Portals 渲染到 body 上。
// fixed 元素要放在 body 上,有更好的浏览器兼容性。
return ReactDOM.createPortal(
<div className="modal">{this.props.children}</div>,
document.body // DOM 节点
)
}
}
export default App
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 使用场景
overflow:hidden(即父组件开启了BFC,限制了子组件的展示,这时子组件就可以用Portals逃离父组件)- 父组件z-index值太小
- fixed需要放在body第一层级
# 3.4 context
公共信息(语言、主题)如何传递给每个组件
用props太繁琐
用redux小题大做
import React from 'react'
// 创建 Context 填入默认值(任何一个 js 变量)
const ThemeContext = React.createContext('light')
// 底层组件 - 函数是组件
function ThemeLink (props) {
// const theme = this.context // 会报错。函数式组件没有实例,即没有 this
// 函数式组件可以使用 Consumer
return <ThemeContext.Consumer>
{ value => <p>link's theme is {value}</p> }
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
}
// 底层组件 - class 组件
class ThemedButton extends React.Component {
// 指定 contextType 读取当前的 theme context。
// static contextType = ThemeContext // 也可以用 ThemedButton.contextType = ThemeContext
render() {
const theme = this.context // React 会往上找到最近的 theme Provider,然后使用它的值。
return <div>
<p>button's theme is {theme}</p>
</div>
}
}
ThemedButton.contextType = ThemeContext // 指定 contextType 读取当前的 theme context。
// 中间的组件再也不必指明往下传递 theme 了。
function Toolbar(props) {
return (
<div>
<ThemedButton />
<ThemeLink />
</div>
)
}
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
theme: 'light'
}
}
render() {
return <ThemeContext.Provider value={this.state.theme}>
<Toolbar />
<hr/>
<button onClick={this.changeTheme}>change theme</button>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
}
changeTheme = () => {
this.setState({
theme: this.state.theme === 'light' ? 'dark' : 'light'
})
}
}
export default App
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# 异步组件
import()React.lazyReact.Suspense
import React from 'react'
const ContextDemo = React.lazy(() => import('./ContextDemo'))
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
return <div>
<p>引入一个动态组件</p>
<hr />
<React.Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<ContextDemo/>
</React.Suspense>
</div>
// 1. 强制刷新,可看到 loading (看不到就限制一下 chrome 网速)
// 2. 看 network 的 js 加载
}
}
export default App
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
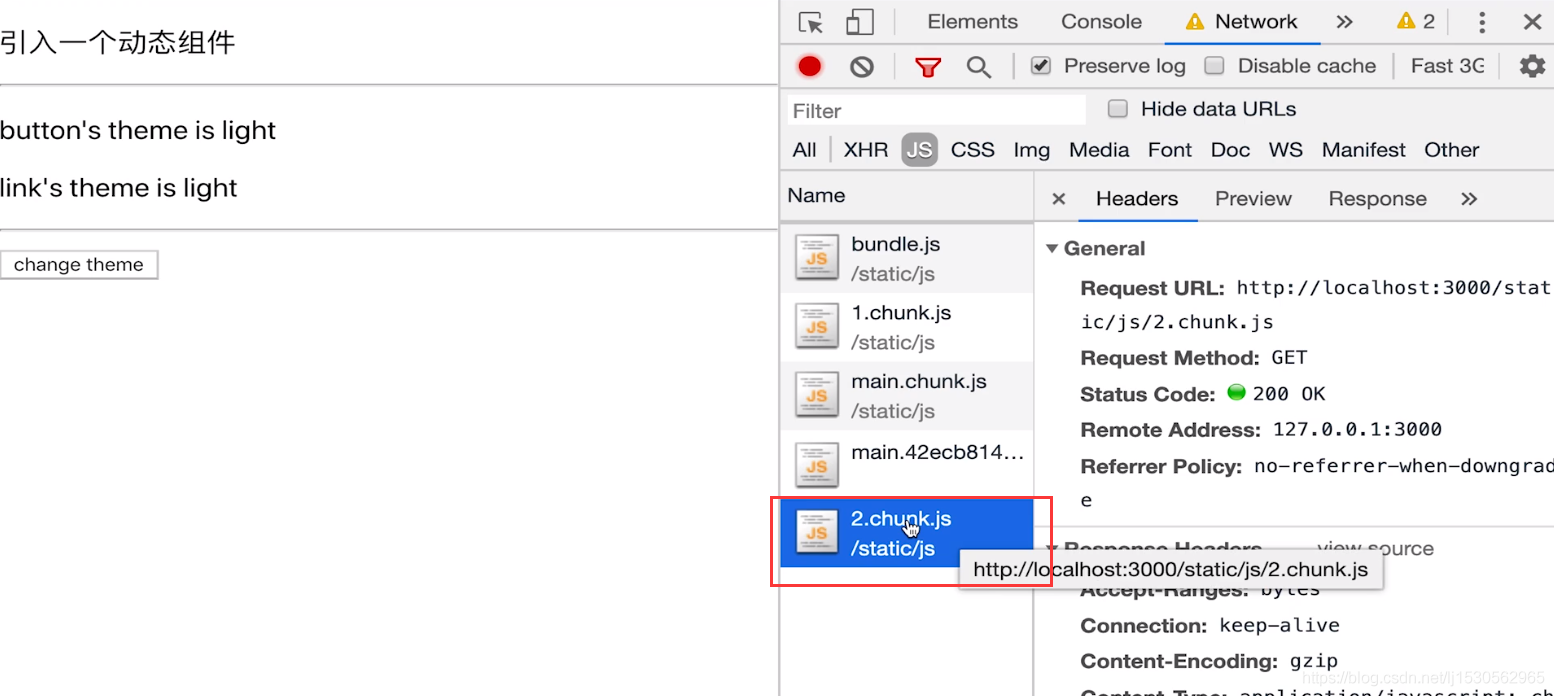
强制刷新,可看到 loading (看不到就限制一下 chrome 网速)
 看 network 的 js 加载,会单独有个js
看 network 的 js 加载,会单独有个js
# 3.5 性能优化
性能优化,永远都是面试的重点
性能优化对于React更加重要
回顾讲setState时重点强调的不可变值
# 3.5.1 SCU基本用法
- React默认:父组件有更新,子组件无论数据是否改变则无条件也更新
- SCU默认返回true
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (nextState.count !== this.state.count) {
return true //可以渲染
}
return false //不重复渲染
}
2
3
4
5
6
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class Input extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
title: ''
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<input value={this.state.title} onChange={this.onTitleChange}/>
<button onClick={this.onSubmit}>提交</button>
</div>
}
onTitleChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
title: e.target.value
})
}
onSubmit = () => {
const { submitTitle } = this.props
submitTitle(this.state.title) // 'abc'
this.setState({
title: ''
})
}
}
// props 类型检查
Input.propTypes = {
submitTitle: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
class List extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
const { list } = this.props
return <ul>{list.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={item.id}>
<span>{item.title}</span>
</li>
})}</ul>
}
}
// props 类型检查
List.propTypes = {
list: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.object).isRequired
}
class Footer extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
return <p>
{this.props.text}
{this.props.length}
</p>
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('footer did update')
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (nextProps.text !== this.props.text
|| nextProps.length !== this.props.length) {
return true // 可以渲染
}
return false // 不重复渲染
}
// React 默认:父组件有更新,子组件则无条件也更新!!!
// 性能优化对于 React 更加重要!
// SCU 一定要每次都用吗?—— 需要的时候才优化
}
class TodoListDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 状态(数据)提升
this.state = {
list: [
{
id: 'id-1',
title: '标题1'
},
{
id: 'id-2',
title: '标题2'
},
{
id: 'id-3',
title: '标题3'
}
],
footerInfo: '底部文字'
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<Input submitTitle={this.onSubmitTitle}/>
<List list={this.state.list}/>
<Footer text={this.state.footerInfo} length={this.state.list.length}/>
</div>
}
onSubmitTitle = (title) => {
this.setState({
list: this.state.list.concat({
id: `id-${Date.now()}`,
title
})
})
}
}
export default TodoListDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
# 3.5.2 SCU一定要配合不可变值
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import _ from 'lodash'
class Input extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
title: ''
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<input value={this.state.title} onChange={this.onTitleChange}/>
<button onClick={this.onSubmit}>提交</button>
</div>
}
onTitleChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
title: e.target.value
})
}
onSubmit = () => {
const { submitTitle } = this.props
submitTitle(this.state.title)
this.setState({
title: ''
})
}
}
// props 类型检查
Input.propTypes = {
submitTitle: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
class List extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
const { list } = this.props
return <ul>{list.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={item.id}>
<span>{item.title}</span>
</li>
})}</ul>
}
// 增加 shouldComponentUpdate
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// _.isEqual 做对象或者数组的深度比较(一次性递归到底),深度比较较耗费性能,可以使用浅比较,设计state层级尽量设计得不要太深,扁平一些
if (_.isEqual(nextProps.list, this.props.list)) {
// 相等,则不重复渲染
return false
}
return true // 不相等,则渲染
}
}
// props 类型检查
List.propTypes = {
list: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.object).isRequired
}
class TodoListDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
list: [
{
id: 'id-1',
title: '标题1'
},
{
id: 'id-2',
title: '标题2'
},
{
id: 'id-3',
title: '标题3'
}
]
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<Input submitTitle={this.onSubmitTitle}/>
<List list={this.state.list}/>
</div>
}
onSubmitTitle = (title) => {
// 正确的用法
this.setState({
list: this.state.list.concat({
id: `id-${Date.now()}`,
title
})
})
// // 为了演示 SCU ,故意写的错误用法,会导致SCU不执行,因为state值push后和setState一致
// this.state.list.push({
// id: `id-${Date.now()}`,
// title
// })
// this.setState({
// list: this.state.list
// })
}
}
export default TodoListDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
# 3.5.3 SCU使用总结
SCU默认返回true,即React默认重新渲染所有子组件
必须配合“不可变值”一起使用
可先不用SCU,有性能问题时再考虑使用
# 3.5.4 PureComponent和React.memo
PureComponent,SCU中实现了浅比较
memo,函数组件中的PureComponent
浅比较已适用大部分情况(尽量不要深度比较)
//PureComponentDemo.js
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class Input extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
title: ''
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<input value={this.state.title} onChange={this.onTitleChange}/>
<button onClick={this.onSubmit}>提交</button>
</div>
}
onTitleChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
title: e.target.value
})
}
onSubmit = () => {
const { submitTitle } = this.props
submitTitle(this.state.title)
this.setState({
title: ''
})
}
}
// props 类型检查
Input.propTypes = {
submitTitle: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
class List extends React.PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
const { list } = this.props
return <ul>{list.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={item.id}>
<span>{item.title}</span>
</li>
})}</ul>
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {/*浅比较*/}
}
// props 类型检查
List.propTypes = {
list: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.object).isRequired
}
class TodoListDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
list: [
{
id: 'id-1',
title: '标题1'
},
{
id: 'id-2',
title: '标题2'
},
{
id: 'id-3',
title: '标题3'
}
]
}
}
render() {
return <div>
<Input submitTitle={this.onSubmitTitle}/>
<List list={this.state.list}/>
</div>
}
onSubmitTitle = (title) => {
// 正确的用法
this.setState({
list: this.state.list.concat({
id: `id-${Date.now()}`,
title
})
})
// // 为了演示 SCU ,故意写的错误用法
// this.state.list.push({
// id: `id-${Date.now()}`,
// title
// })
// this.setState({
// list: this.state.list
// })
}
}
export default TodoListDemo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103

# 3.5.5 不可变值immutable.js
彻底拥抱“不可变值”
基于共享数据(不是深拷贝),速度好
有一定学习和迁移成本,按需使用
//immutable.js示例
const map1 = Immutable.Map({ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 })
const map2 = map1.set('b', 50)
map1.get('b') // 2
map2.get('b') // 50
2
3
4
5
# 3.5.6 性能优化-小结
- 面试重点,且涉及React涉及理念
SCUPureComponentmemoimmutable.js- 按需使用 & state层级
# 3.6 高阶组件HOC
# 3.6.1 关于组件公共逻辑的抽离
mixin,已被React弃用- 高阶组件``HOC`
Render Props
# 3.6.2 高阶组件基本用法
//高阶组件不是一种功能,而是一种模式
const HOCFactory = (Component) => {
class HOC extends React.Component {
//在此定义多个组件的公共逻辑
render(){
return <Component { ...this.props } />//返回拼装的结果
}
}
return HOC
}
const EnhancedComponent1=HOCFactory(WrappedComponent1)
const EnhancedComponent2 = HOCFactory(WrappedComponent2)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import React from 'react'
// 高阶组件
const withMouse = (Component) => {
class withMouseComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = { x: 0, y: 0 }
}
handleMouseMove = (event) => {
this.setState({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
})
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{ height: '500px' }} onMouseMove={this.handleMouseMove}>
{/* 1. 透传所有 props 2. 增加 mouse 属性 */}
<Component {...this.props} mouse={this.state}/>
</div>
)
}
}
return withMouseComponent
}
const App = (props) => {
const a = props.a
const { x, y } = props.mouse // 接收 mouse 属性
return (
<div style={{ height: '500px' }}>
<h1>The mouse position is ({x}, {y})</h1>
<p>{a}</p>
</div>
)
}
export default withMouse(App) // 返回高阶函数
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 3.6.3 Redux connect是高阶组件
//connect使用示例
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
// connect 是高阶组件
const VisibleTodoList = connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
) (TodoList)
export default VisibleTodoList
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
//connect源码
export const connect = (mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) => (WrappedComponent) =>{
class Connect extends Component {
constructor () {
super()
this.state = {
allProps: {}
}
}
/*中间省略 N 行代码*/
render () {
return <WrappedComponent {...this.state.allProps} />
}
}
return Connect
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 3.7 Renders Props

import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class Mouse extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = { x: 0, y: 0 }
}
handleMouseMove = (event) => {
this.setState({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
})
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{ height: '500px' }} onMouseMove={this.handleMouseMove}>
{/* 将当前 state 作为 props ,传递给 render (render 是一个函数组件) */}
{this.props.render(this.state)}
</div>
)
}
}
Mouse.propTypes = {
render: PropTypes.func.isRequired // 必须接收一个 render 属性,而且是函数
}
const App = (props) => (
<div style={{ height: '500px' }}>
<p>{props.a}</p>
<Mouse render={
/* render 是一个函数组件 */
({ x, y }) => <h1>The mouse position is ({x}, {y})</h1>
}/>
</div>
)
/**
* 即,定义了 Mouse 组件,只有获取 x y 的能力。
* 至于 Mouse 组件如何渲染,App 说了算,通过 render prop 的方式告诉 Mouse 。
*/
export default App
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# HOC vs Render Props
HOC:模式简单,但会增加组件层级
Render Props:代码简洁,学习成本较高
按需使用
# 4.Redux
- 和Vuex作用相同,但比Vuex学习成本高
- 不可变值,纯函数
- 面试常考
# 4.1 基本概念
storestateactionreducer
//https://www.redux.org.cn/
import { createStore } from 'redux';
/**
* 这是一个 reducer,形式为 (state, action) => state 的纯函数。
* 描述了 action 如何把 state 转变成下一个 state。
*
* state 的形式取决于你,可以是基本类型、数组、对象、
* 甚至是 Immutable.js 生成的数据结构。惟一的要点是
* 当 state 变化时需要返回全新的对象,而不是修改传入的参数。
*
* 下面例子使用 `switch` 语句和字符串来做判断,但你可以写帮助类(helper)
* 根据不同的约定(如方法映射)来判断,只要适用你的项目即可。
*/
function counter(state = 0, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + 1;
case 'DECREMENT':
return state - 1;
default:
return state;
}
}
// 创建 Redux store 来存放应用的状态。
// API 是 { subscribe, dispatch, getState }。
let store = createStore(counter);
// 可以手动订阅更新,也可以事件绑定到视图层。
store.subscribe(() =>
console.log(store.getState())
);
// 改变内部 state 惟一方法是 dispatch 一个 action。
// action 可以被序列化,用日记记录和储存下来,后期还可以以回放的方式执行
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
// 1
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
// 2
store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' });
// 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
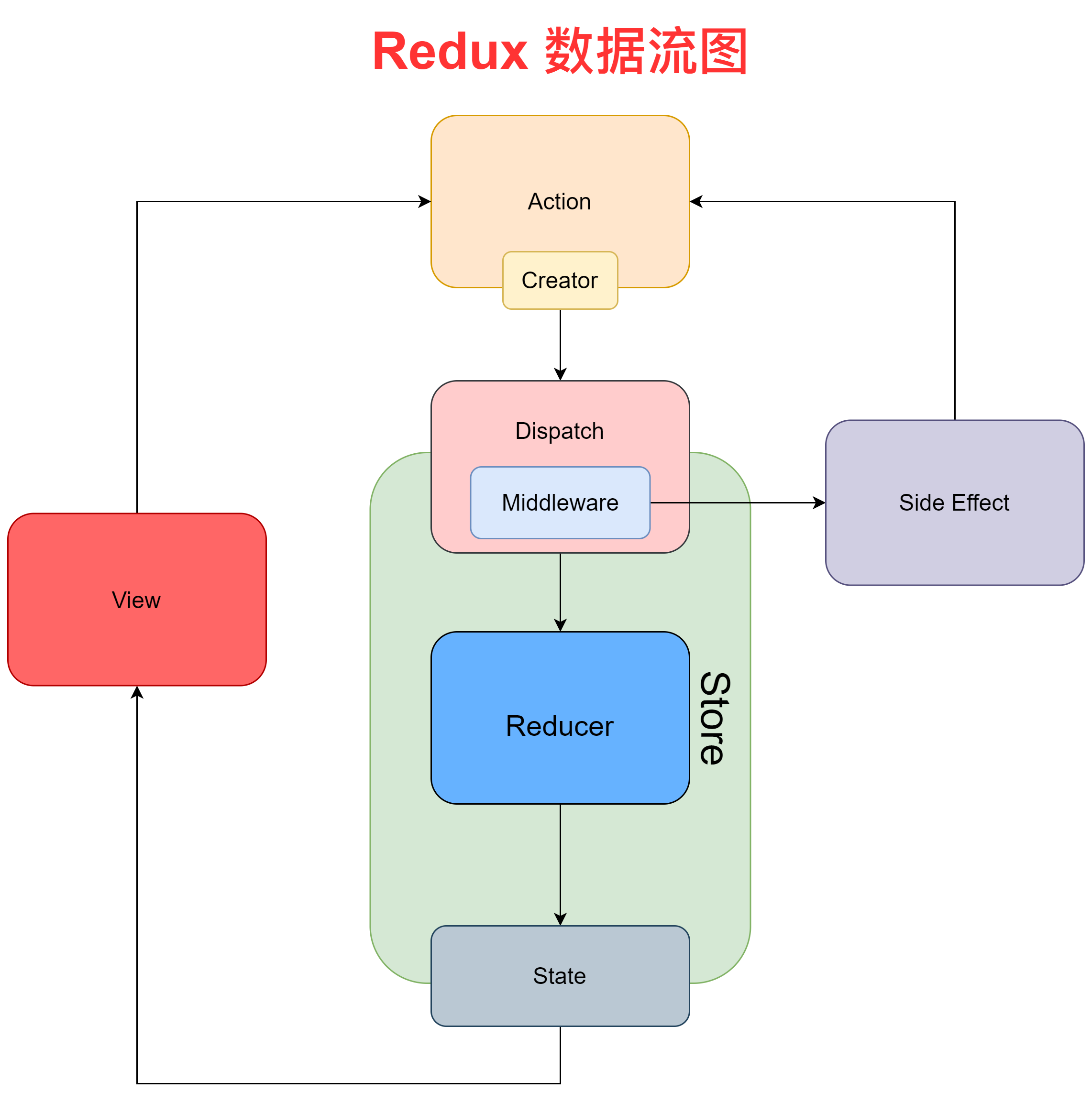
# 4.2 单项数据流
dispatch(action)
reducer -> newState
subscribe触发通知
dispatch一个action会触发reducer,reducer更新状态,注意不可变值,再触发订阅通知,渲染到页面
# 4.3 react-redux
ProviderconnectmapStateToPropsmapDispatchToProps
//index.js
import React from 'react'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import todoApp from './reducers'
import App from './components/App'
let store = createStore(todoApp)
export default function () {
return <Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//AddTodo.js
import React from 'react'
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { addTodo } from '../actions'
// 函数组件,接收 props 参数
let AddTodo = ({ dispatch }) => {
// dispatch 即 props.dispatch
let input
return (
<div>
<form
onSubmit={e => {
e.preventDefault()
if (!input.value.trim()) {
return
}
// 创建一个 todo
dispatch(addTodo(input.value))
input.value = ''
}}
>
<input
ref={node => {
input = node
}}
/>
<button type="submit">
Add Todo
</button>
</form>
</div>
)
}
// connect 高阶组件 ,将 dispatch 作为 props 注入到 AddTodo 组件中
AddTodo = connect()(AddTodo)
export default AddTodo
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
//VisibleTodoList.js
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { toggleTodo } from '../actions'
import TodoList from '../components/TodoList'
// 不同类型的 todo 列表
const getVisibleTodos = (todos, filter) => {
switch (filter) {
case 'SHOW_ALL':
return todos
case 'SHOW_COMPLETED':
return todos.filter(t => t.completed)
case 'SHOW_ACTIVE':
return todos.filter(t => !t.completed)
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
// state 即 vuex 的总状态,在 reducer/index.js 中定义
return {
// 根据完成状态,筛选数据
todos: getVisibleTodos(state.todos, state.visibilityFilter)
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => {
return {
// 切换完成状态
onTodoClick: id => {
dispatch(toggleTodo(id))
}
}
}
// connect 高阶组件,将 state 和 dispatch 注入到组件 props 中
const VisibleTodoList = connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(TodoList)
export default VisibleTodoList
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 4.4 异步action
//同步 action
export const addTodo = text =>{
//返回 action 对象
return {
type: 'ADD_TODO',
id: nextTodoId++,
text
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//异步 action
export const addTodoAsync = text =>{
//返回函数,其中有 dispatch 参数
return (dispatch) => {
//ajax 异步获取数据
fetch(url).then(res => {
//执行异步 action
dispatch(addTodo(res.text))
})
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
异步action使用前要引入中间件
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import rootReducer from './reducers/index';
//创建 store 时,作为中间件引入 redux-thunk
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
2
3
4
5
6
# 4.5 中间件
Redux中间件有:
- redux-thunk
- redux-promise
- redux-saga
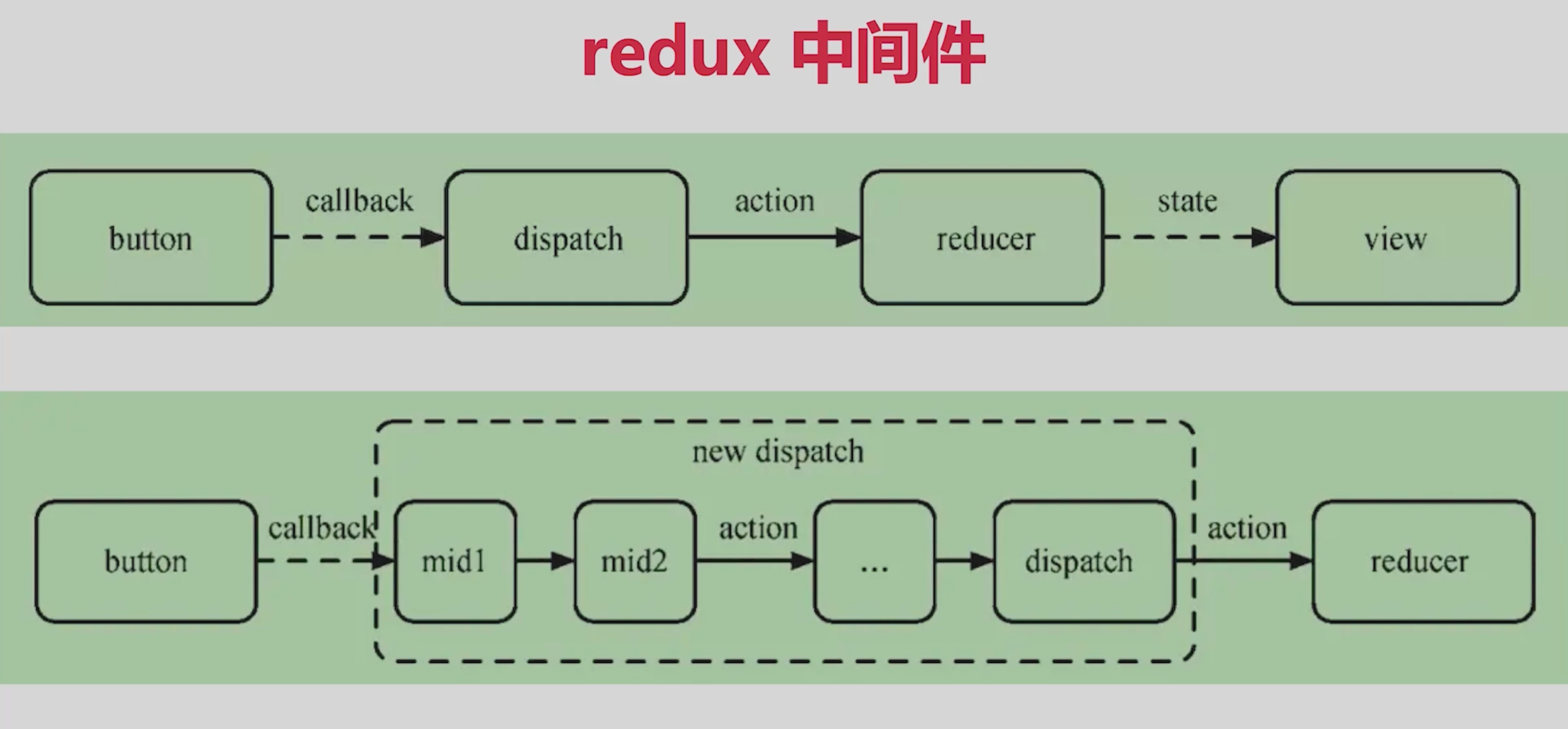
//redux中间件-示例
import { applyMiddleware, createStore } from 'redux';
import createLogger from 'redux-logger';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
const logger = createLogger();
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(thunk, logger)//会按顺序执行
);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
//redux中间件-logger实现
//自己修改 dispatch,增加 logger
let next = store.dispatch;
store.dispatch = function dispatchAndLog(action) {
console.log('dispatching', action);
next(action);
console.log('next state', store.getState());
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 5.React-router
面试考点并不多(前提是熟悉React)
路由模式(hash,H5 history),同vue-router
路由配置(动态路由、懒加载),同vue-router
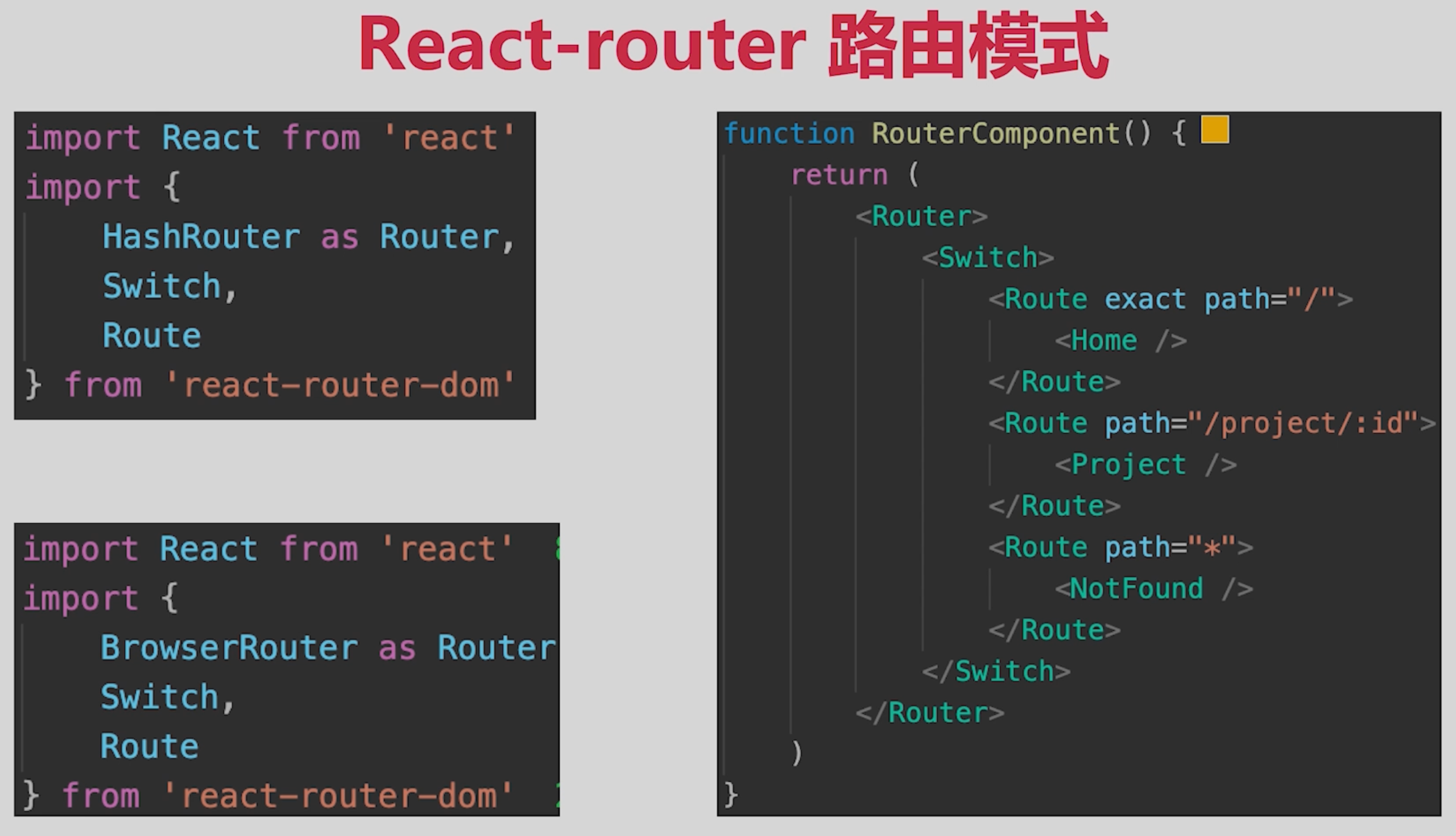
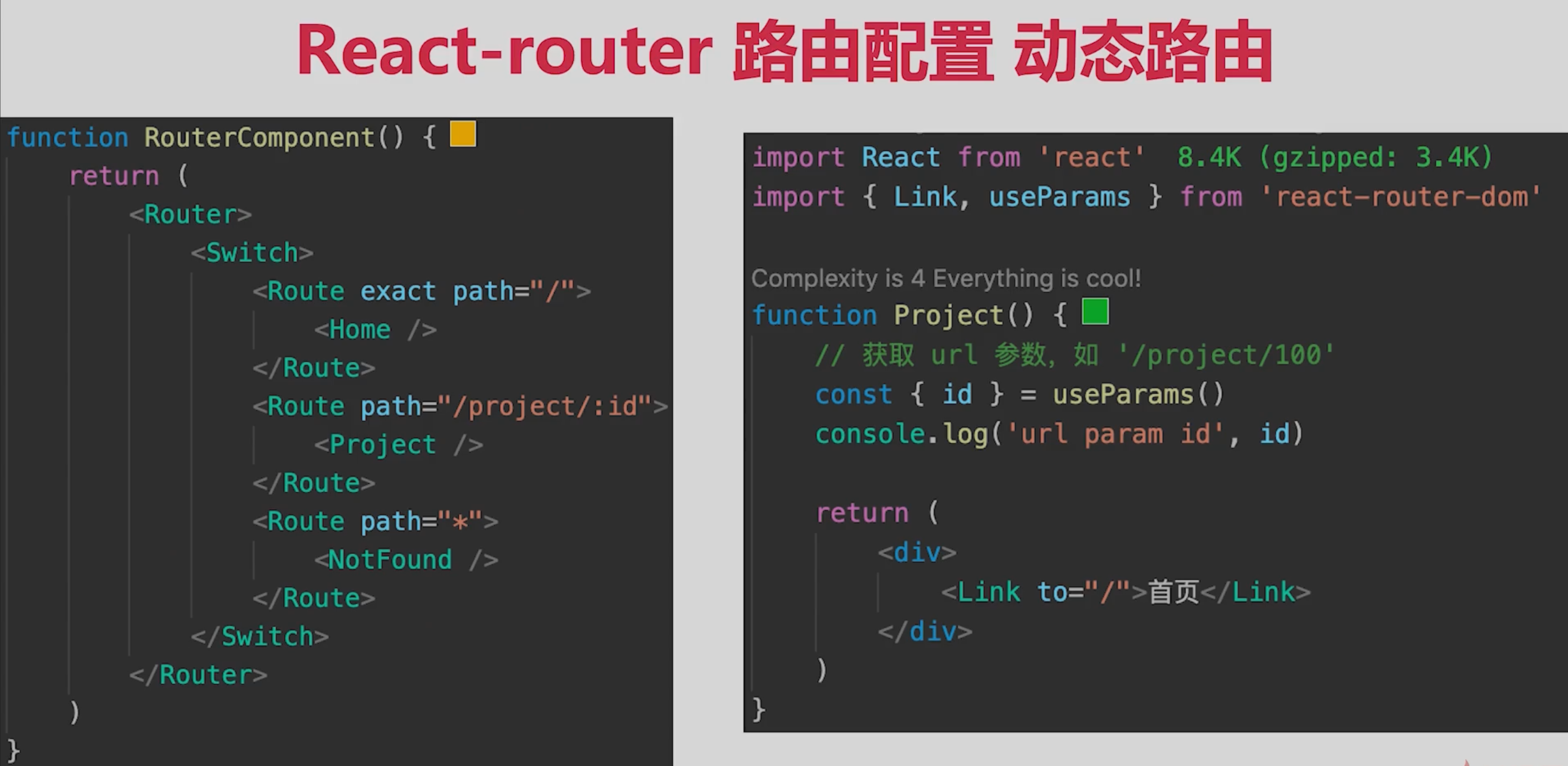
# 5.1 路由模式
- hash模式(默认),如http://abc.com/#/user/10
- H5 history模式,如http://abc.com/user/20
- 后者需要server端支持,因此无特殊需求可选择前者
- toC客户端一般H5 history,toB控制后台一般hash


# 5.2 React-router总结
- 路由模式(hash、H5 history)
- 路由配置(动态路由、懒加载)
- 掌握基本使用
